In the precision manufacturing field of injection molding, injection molds serve as crucial tools for shaping product forms. The structural design and functional implementation of these molds are of utmost importance. This article will take you on a deep dive into the seven core components of injection molds, analyzing their vital roles in the injection molding process one by one.
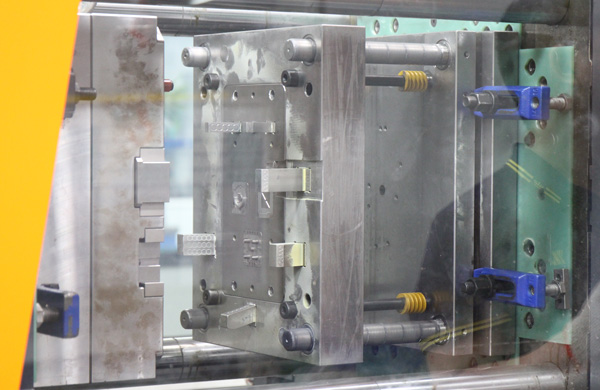
Forming parts, including key components such as front and rear mold cores and mold inserts, directly participate in the plastic molding process, coming into close contact with molten plastic to ultimately shape the precise contours of products. Therefore, the processing accuracy of these parts is extremely demanding, as any slight deviation can affect the final quality of the product.
The gating system, consisting of components such as locating rings and sprue bushings, is the bridge that allows molten plastic to enter the mold cavity from the injection molding machine. It is responsible for uniformly and quickly filling the plastic into the mold cavity, while also bearing the crucial task of transmitting injection pressure to ensure that the plastic fully fills and closely adheres to the mold surface.
The ejection system, comprising parts such as ejector pins, ejector pin plates, and ejector pin retaining plates, is the key mechanism for ensuring the smooth ejection of molded products. The design must fully consider the ease of ejecting the plastic parts, avoiding any factors that could lead to deformation, cracking, or scratching of the parts. It ensures that the ejection process is both flexible and reliable, while also facilitating subsequent replacement and maintenance.
Cooling and heating mechanisms, encompassing components such as water nozzles, water channel tubes, and heater plates, are crucial for regulating mold temperature and ensuring plastic part quality. Precise control of mold temperature can effectively shorten molding cycles, reduce product defects such as shrinkage and deformation, and thereby enhance overall production efficiency and product quality.
Structural parts, such as fixed mold plates, movable mold plates, backing plates, and mold bushes, form the skeleton of the mold structure, responsible for securely combining the forming parts into a single unit. They ensure that the mold maintains stable performance and accuracy even under high-pressure, high-temperature injection molding conditions.
Guiding parts, primarily consisting of guide posts and guide bushes, are the core of mold positioning and guidance. They ensure precise alignment between the movable and fixed molds, maintaining a high degree of positional consistency even through multiple opening and closing cycles, providing a solid guarantee for the precise molding of plastic parts.
Fastening parts, including standardized components such as screws and pins, are the links that connect and secure the various components of the mold. They not only ensure the integrity of the mold structure but also facilitate mold assembly, disassembly, and maintenance, making them an indispensable part of injection molds.
In summary, the seven components of injection molds each have their own roles, collectively forming an efficient and precise injection molding system. A deep understanding of the functions and roles of these components is of great significance for optimizing mold design, enhancing product quality, and improving production efficiency.